Run Docker-in-Docker in a Build stage
CI pipelines that use a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure need Docker-in-Docker (DinD) if you need to run Docker commands as part of the build process. For example, if you want to build images from two separate codebases in the same pipeline: One with a Build and Push to Docker step and another with Docker commands in a Run step.
To configure DinD in Harness CI, you need to add a DinD Background step and a Run step that runs Docker commands to your pipeline.
Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure required
Docker-in-Docker (DinD) with privileged mode is necessary only when using a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure. For other infrastructure types, you can run Docker commands directly on the host.
Privileged mode required
Docker-in-Docker must run in privileged mode to work properly. Be aware that privileged mode provides full access to the host environment. For more information, go to the Docker documentation on Runtime Privilege and Linux Capabilities.
You can't use DinD on platforms that don't support privileged mode, such as those that run containers on Windows.
Prepare a pipeline for DinD
You need a pipeline with a Build stage that uses a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure. DinD is necessary for Kubernetes cluster build infrastructures only. For other infrastructure types, you can run Docker commands directly on the host.
To demonstrate how to set up DinD in Harness CI, this topic creates a pipeline that includes a DinD Background step and a Run step that builds and pushes an image. If you want to follow this example, you can configure your Build stage as follows:
-
In your pipeline, select the Build stage, and then select the Overview tab.
-
Under Stage Details, disable Clone Codebase. The example pipeline created in this topic doesn't use a default codebase; instead, the codebase is cloned by commands in the Run step.
-
Under Shared Paths, add the following two paths:
/var/run/var/lib/docker
-
Expand Advanced, and add stage variables for your Docker Hub Personal Access Token (PAT) and any other values that you want to parameterize.
For passwords and Personal Access Tokens, select Secret as the variable type. For example, to add the Docker Hub PAT variable:
- Type: Select Secret.
- Name: Enter a name, such as
Docker Hub PAT. - Value: Select a Harness text secret containing your Docker Hub PAT.
-
Select the Infrastructure tab.
-
Under Infrastructure, select Kubernetes, and then configure a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure.
Add a DinD Background step
In your Build stage, select the Execution tab, and add a Background step configured as follows:
- For Name, enter
dind_Service. - For Container Registry, select your Docker connector.
- For Image, enter the name and tag for the image that you want to use to run DinD, such as docker:dind. In some cases, an FQN may be necessary. More information can be found below about setting up the registry and image.
- Under Additional Configuration, select Privileged. Privileged mode is required Docker-in-Docker to run correctly.
- In Entry Point, you can provide a list of arguments, if needed. For example, the entry point for the
docker:dindimage isdocker-entrypoint.sh. If you want to add a--mtuargument, you would include both the image entry point and the additional argument in the Entry Point specification.
- Visual
- YAML
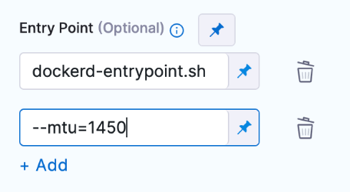
entrypoint:
- docker-entrypoint.sh
- "--mtu=1450"
Add a Docker Run step
After the Background step, add a Run step to run your Docker commands. Configure the Run step settings as follows:
-
Enter a Name.
-
For Container Registry, select your Docker connector.
-
For Image, enter the name and tag for the Docker image, with the Docker binary, that you want to use to execute the content of Command. In some cases, an FQN may be necessary. More information can be found below about setting up the registry and image.
-
In Command, enter the shell commands you want to run in this step.
For example, the following commands clone a Git repo, build an image, and push the image to a Docker registry:
apk add git
git --version
git clone https://github.com/$GITHUB_USERNAME/$GITHUB_REPO
cd $GITHUB_REPO
echo $DOCKERHUB_PAT > my_password.txt
cat my_password.txt | docker login --username $DOCKERHUB_USERNAME --password-stdin
docker build -t $DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL
docker tag $DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL $DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/$DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL:<+pipeline.sequenceId>
docker push $DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/$DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL:<+pipeline.sequenceId>Variables and expressionsThe variables referenced in this command, such as
$DOCKERHUB_PAT, refer to stage variables that reference string values or Harness text secrets.These commands also use
<+pipeline.sequenceId>, which is a Harness expression that prints the incremental build identifier.
Wait for the container to initialize
When the build runs and the container starts, the software inside the container takes time to initialize and start accepting connections. Give the service adequate time to initialize before trying to connect. To do this, you can use a while loop in your Command, such as:
while ! docker ps ;do
echo "Docker not available yet"
done
echo "Docker Service Ready"
docker ps
You can also add steps to your pipeline that run health checks on background services.
DinD and Docker container logs
When you run your pipeline, you can review the step logs on the Build details page.
Container Registry and Image
The build environment must have the necessary binaries for the DinD step. Depending on the stage's build infrastructure, DinD steps can use binaries that exist in the build environment, or use Container Registry and Image to pull an image, such as a public or private Docker image, that contains the required binaries.
####When are Container Registry and Image required?
The stage's build infrastructure determines whether these fields are required or optional:
- Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure: Container Registry and Image are always required.
- Local runner build infrastructure: Run Tests steps can use binaries available on the host machine. The Container Registry and Image are required if the machine doesn't have the binaries you need.
- Self-managed AWS/GCP/Azure VM build infrastructure: Run Tests steps can use binaries that you've made available on your build VMs. The Container Registry and Image are required if the VM doesn't have the necessary binaries. These fields are located under Additional Configuration for stages that use self-managed VM build infrastructure.
- Harness Cloud build infrastructure: Run Tests steps can use binaries available on Harness Cloud machines, as described in the image specifications. The Container Registry and Image are required if the machine doesn't have the binaries you need. These fields are located under Additional Configuration for stages that use Harness Cloud build infrastructure.
What are the expected values for Container Registry and Image
For Container Registry settings, provide a Harness container registry connector, such as a Docker connector, that connects to a container registry, such as Docker Hub, where the Image is located.
For Image, provide the FQN (fully-qualified name) or artifact name and tag of the Docker image to use when this step runs commands, for example us-docker.pkg.dev/gar-prod-setup/harness-public/harness/cache:latest or maven:3.8-jdk-11. If you don't include a tag, Harness uses the latest tag. Depending on the connector and feature flags set, an FQN may be required.
You can use any Docker image from any Docker registry, including Docker images from private registries. Different container registries require different name formats, for example:
-
Docker Registry: Input the name of the artifact you want to deploy, such as
library/tomcat. Wildcards aren't supported. FQN is required for images in private container registries. -
ECR: Input the FQN of the artifact you want to deploy. Images in repos must reference a path, for example:
40000005317.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/todolist:0.2. -
GAR: Input the FQN of the artifact you want to deploy. Images in repos must reference a path starting with the project ID that the artifact is in, for example:
us-docker.pkg.dev/gar-prod-setup/harness-public/harness/cache:latest.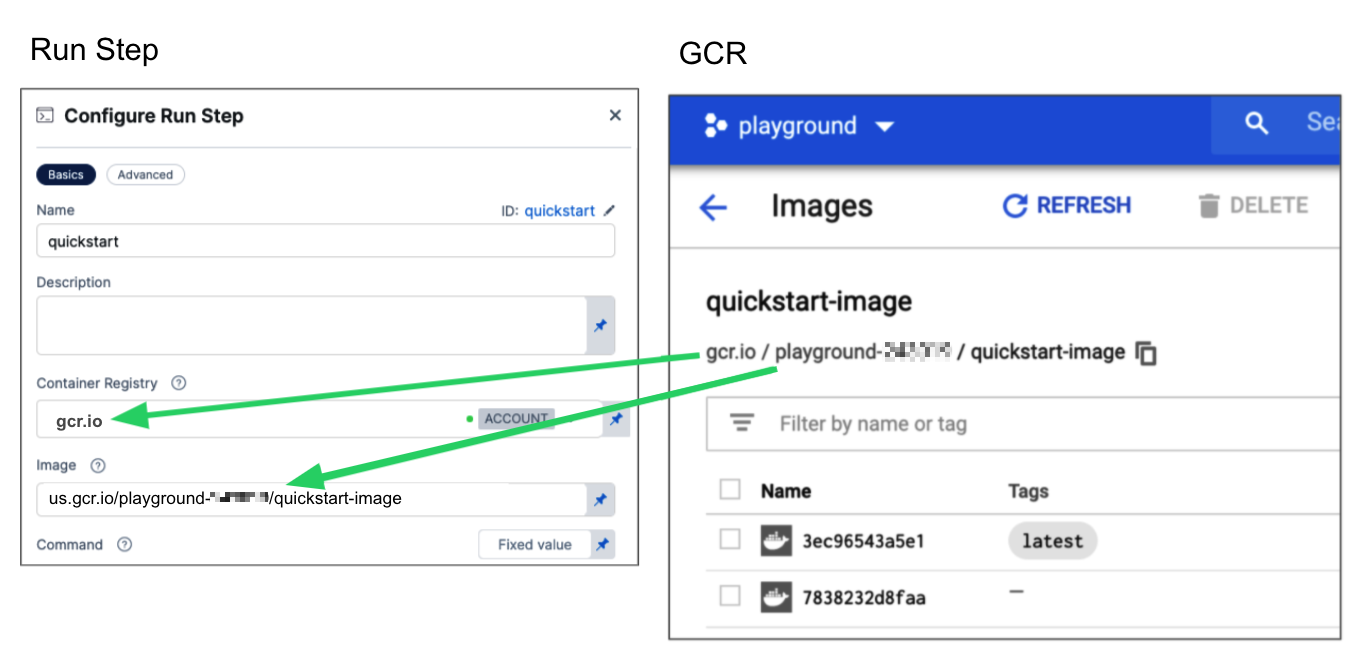
Configuring a Container Registry and Image settings.
Customers who want to utilize non-FQN references for non public Docker-registry connectors will need to contact Harness Support to add the feature flags, CI_REMOVE_FQN_DEPENDENCY_FOR_PRIVATE_REGISTRY_CONNECTOR_DOCKER and CI_REMOVE_FQN_DEPENDENCY.
Pulling images from JFrog Artifactory Docker registries
If you need to pull images from a JFrog Artifactory Docker registry, create a Docker connector that connects to your JFrog instance. Don't use the Harness Artifactory connector - The Artifactory connector only supports JFrog non-Docker registries.
To create a Docker connector for a JFrog Docker registry:
- Go to Connectors in your Harness project, organization, or account resources, and select New Connector.
- Select Docker Registry under Artifact Repositories.
- Enter a Name for the connector. The Description and Tags are optional.
- For Provider Type, Select Other.
- In Docker Registry URL, enter your JFrog URL, such as
https://mycompany.jfrog.io. - In the Authentication settings, you must use Username and Password authentication.
- Username: Enter your JFrog username.
- Password: Select or create a Harness text secret containing the password corresponding with the Username.
- Complete any other settings and save the connector. For information all Docker Registry connector settings, go to the Docker connector settings reference.
One completed, please remember to use the FQN location of the image unless you have set the appropriate feature flags as listed above
The JFrog URL format depends on your Artifactory configuration, and whether your Artifactory instance is local, virtual, remote, or behind a proxy. To get your JFrog URL, you can select your repo in your JFrog instance, select Set Me Up, and get the repository URL from the server name in the docker-login command.
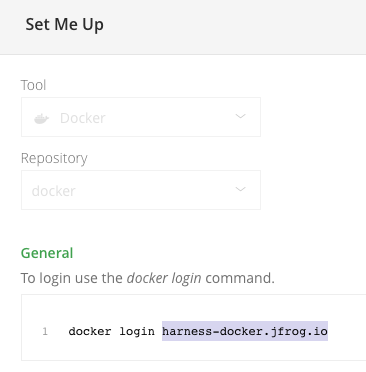
For more information, go to the JFrog documentation on Repository Management and Configuring Docker Repositories.
Pipeline YAML example
The following YAML example defines a pipeline that:
- Uses a Kubernetes cluster build infrastructure.
- Has a Background step that runs DinD
- Has a Run step that runs a series of commands on a Docker image.
This example doesn't use a default codebase (cloneCodebase: false). Instead, the codebase is cloned by commands in the Run step.
pipeline:
name: dind-background-step-demo
identifier: dindbackgroundstepdemo
projectIdentifier: default
orgIdentifier: default
tags: {}
stages:
- stage:
name: build
identifier: build
type: CI
spec:
cloneCodebase: false
execution:
steps:
- step:
type: Background
name: Background
identifier: Background
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_DOCKER_CONNECTOR_ID
image: docker:dind
shell: Sh
privileged: true
- step:
type: Run
name: Run
identifier: Run
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_DOCKER_CONNECTOR_ID
image: docker:run_step_image
shell: Sh
command: |-
while ! docker ps ;do
echo "Docker not available yet"
done
echo "Docker Service Ready"
docker ps
apk add git
git --version
git clone https://github.com/john-doe/$GITHUB_REPO
cd $GITHUB_REPO
echo $DOCKERHUB_PAT > my_password.txt
cat my_password.txt | docker login --username $DOCKERHUB_USERNAME --password-stdin
docker build -t $DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL .
docker tag $DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL $DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/$DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL:<+pipeline.sequenceId>
docker push $DOCKERHUB_USERNAME/$DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL:<+pipeline.sequenceId>
privileged: false
infrastructure:
type: KubernetesDirect
spec:
connectorRef: YOUR_K8S_CLUSTER_CONNECTOR_ID
namespace: YOUR_K8S_NAMESPACE
nodeSelector: {}
os: Linux
sharedPaths:
- /var/run
- /var/lib/docker
variables:
- name: DOCKERHUB_USERNAME
type: String
description: ""
value: jdoe
- name: DOCKERHUB_PAT
type: Secret
description: ""
value: jdoedockerhubpat
- name: GITHUB_USERNAME
type: String
description: ""
value: j-doe
- name: GITHUB_REPO
type: String
description: ""
value: codebaseAlpha
- name: GITHUB_PAT
type: Secret
description: ""
value: jdoegithubpat
- name: DOCKER_IMAGE_LABEL
type: String
description: ""
value: dind-bg-step
Troubleshoot Docker-in-Docker in Harness CI
Go to the CI Knowledge Base for questions and issues related to script execution, using Run steps, and Docker-in-Docker, such as:
- Does CI support running Docker-in-Docker images?
- Can't connect to Docker daemon with Docker-in-Docker Background step.
- Can I use an image that doesn't have a shell in a Run step?
- What does the "Failed to get image entrypoint" error indicate in a Kubernetes cluster build?
- How do I start a service started in a container that would usually be started by the default entry point?